Have you ever wondered how inflation can impact your everyday expenses? In this article, we take a closer look at the relationship between inflation and the cost of living for the average individual or family. As prices rise, goods and services become more expensive, which can have significant implications for your budget. Join us as we explore how inflation affects your purchasing power and strategies to mitigate its impact on your finances.
Impact of Inflation on the Average Individual or Family’s Cost of Living
1. Definition and Explanation of Inflation
Inflation refers to the overall increase in prices of goods and services in an economy over time. It erodes the purchasing power of money, as the same amount of currency can buy fewer goods and services. Inflation can be caused by various factors, such as increased demand, supply shortages, or government policies. It is typically measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks changes in the prices of a basket of common goods and services.
2. Indicators of Inflation
There are several indicators that economists and policymakers monitor to gauge inflation levels. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a widely used indicator, which measures the average change in prices paid by consumers for a representative basket of goods and services. Another commonly used indicator is the Producer Price Index (PPI), which tracks changes in the prices received by producers for their output. Additionally, central banks often keep an eye on core inflation, which excludes volatile factors like food and energy prices, to get a clearer understanding of underlying inflation trends.
3. Factors Affecting Inflation
Inflation can be influenced by various factors. One significant factor is the level of aggregate demand in the economy. When demand exceeds supply, it can lead to price increases. In addition, the cost of production, including wages, raw materials, and energy costs, can impact inflation. Government policies, such as changes in tax rates or monetary policies, can also affect inflation. External factors, such as changes in global commodity prices and exchange rates, can also contribute to inflation in a country.
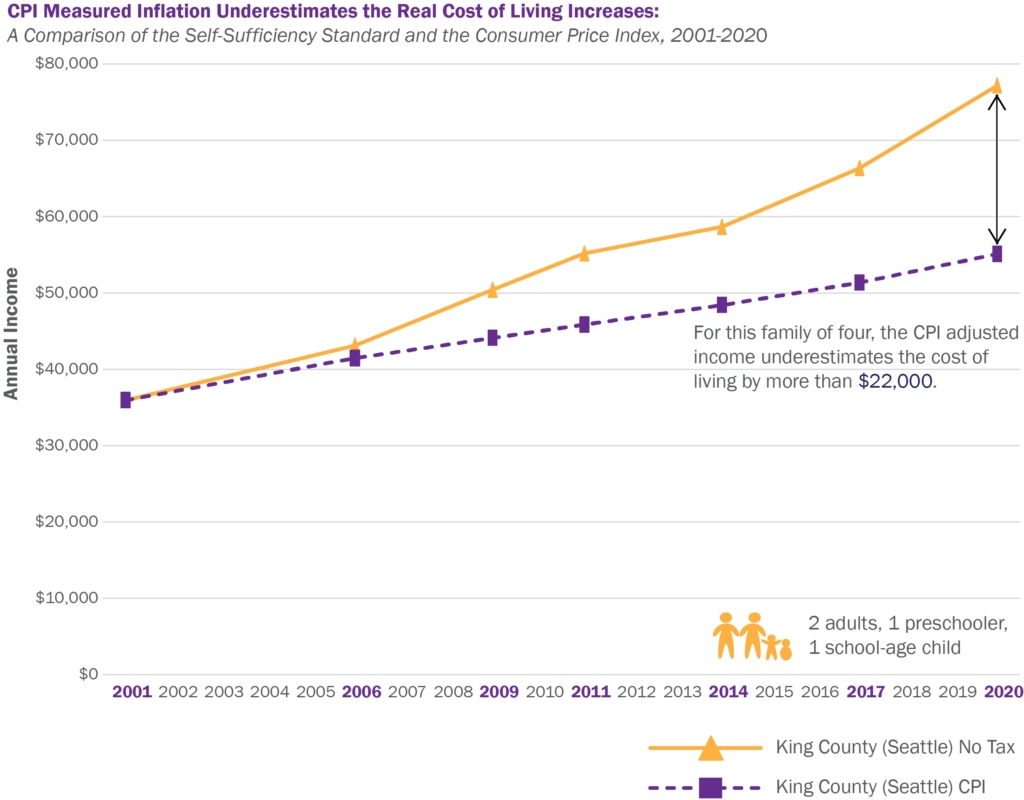
4. Relationship between Inflation and Cost of Living
Inflation directly affects the cost of living for individuals and families. As the general price level increases, the cost of purchasing goods and services also rises. This means that the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services over time, resulting in reduced purchasing power. Inflation can have a profound impact on a household’s budget, as it affects almost every aspect of daily life.
5. Effects on Purchasing Power
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. When prices rise faster than wages or income, individuals and families must spend more money to maintain their current standard of living. This can lead to a decline in the overall purchasing power of their income. For example, if a family’s income increases by 5% but inflation is running at 7%, their purchasing power effectively decreases by 2%. This can make it more challenging to afford essential expenses and save for the future.
6. Changes in Housing Costs
Housing costs, including rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and utilities, are a significant part of the average individual or family’s budget. Inflation can impact housing costs in various ways. Firstly, it can drive up the price of housing itself, making it more expensive to purchase or rent a home. Additionally, inflation can result in higher property taxes and utility bills, further increasing the overall cost of housing. This can squeeze the budgets of individuals and families, particularly if their incomes do not keep pace with rising housing costs.
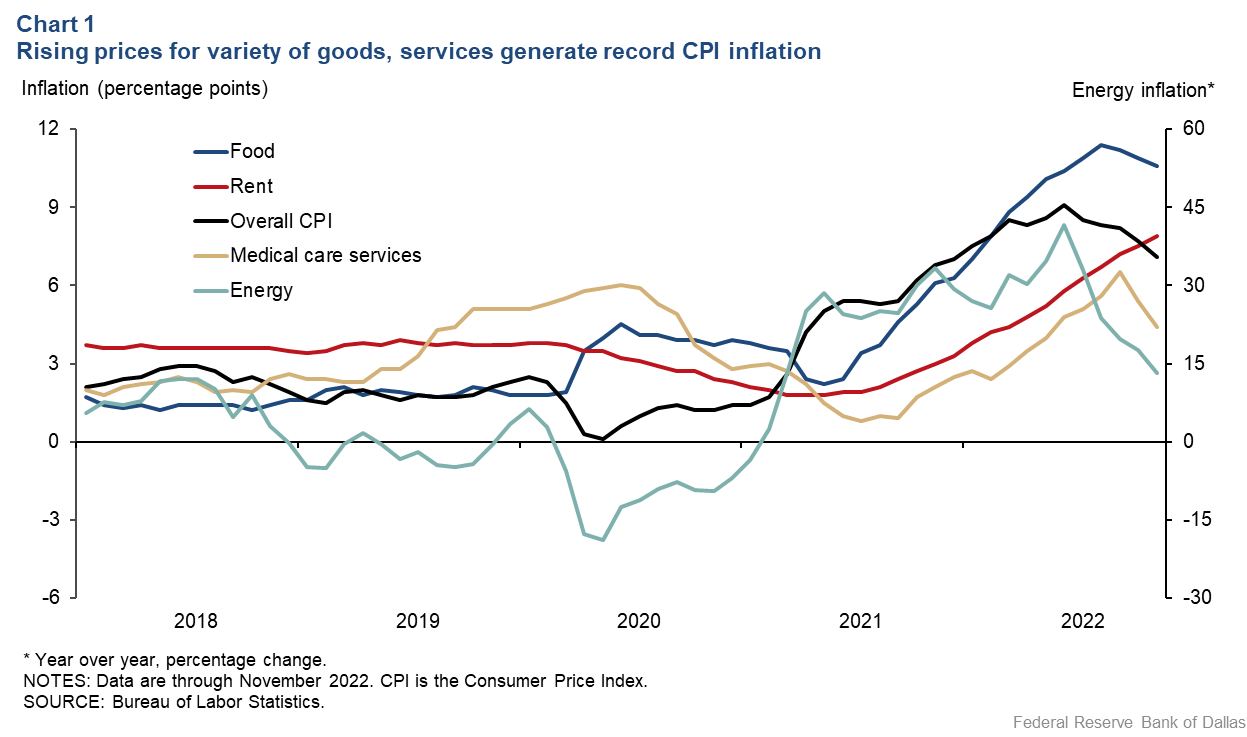
7. Impact on Food and Grocery Expenses
The prices of food and groceries are directly affected by inflation. When the cost of raw materials, transportation, and energy increases, it can lead to higher prices for food products. Inflation can make it more challenging for individuals and families to afford a sufficient and nutritious diet. This can especially impact those on fixed incomes or living paycheck to paycheck. Consequently, individuals and families may need to allocate a larger portion of their budget towards food expenses, potentially compromising spending in other areas.
8. Influence on Transportation Costs
Inflation can also impact transportation costs, affecting both commuting expenses and the cost of goods. Rising fuel prices due to inflation lead to increased costs for commuting, as individuals and families spend more on gasoline or public transportation fares. Moreover, inflation can affect the cost of transporting goods, which may result in higher prices for goods such as groceries and household items. These increased transportation costs can directly impact the cost of living for individuals and families.
9. Effect on Healthcare and Medical Expenses
Medical expenses are a significant burden for many individuals and families. Inflation can further intensify these expenses. Inflation in the healthcare sector can result in higher prices for medical services, prescription drugs, and health insurance premiums. As a result, individuals and families may need to allocate a larger portion of their budget towards healthcare expenses. This can be particularly challenging for those without adequate health insurance coverage, potentially leading to difficult financial decisions related to medical care.
10. Education and Tuition Fees
Inflation can also impact education costs, including tuition fees. The cost of education, from preschool to university, tends to increase over time due to inflation. This can place a significant financial burden on individuals and families planning to pursue further education or support their children’s educational needs. Additionally, inflation can affect the prices of textbooks, school supplies, and other educational resources, further contributing to the overall cost of education.
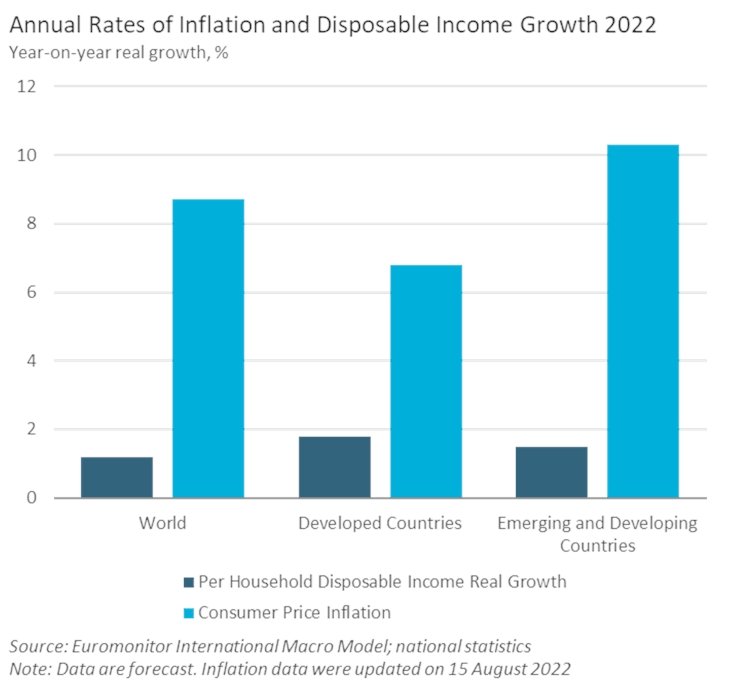
11. Effect on Savings and Investments
Inflation can significantly impact savings and investments. As the value of money decreases over time due to inflation, the purchasing power of savings diminishes. If the returns on investments do not outpace inflation, individuals and families may find that their investments are not generating enough returns to maintain their desired standard of living. This can especially affect retirees who rely on fixed-income investments, potentially jeopardizing their financial security.
12. Impact on Wages and Income
Inflation can have both direct and indirect effects on wages and income. If wages do not keep pace with inflation, individuals and families may experience a decline in their real income. Additionally, inflation can indirectly impact income through its effect on job markets and employment. If inflation leads to higher production costs for businesses, they may respond by reducing hiring or implementing wage freezes. This can limit income growth for individuals and families, further exacerbating the impact of inflation on their cost of living.
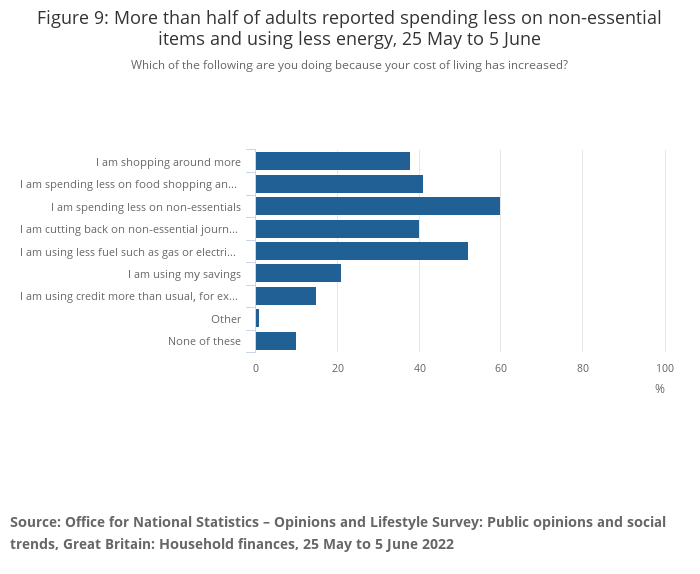
13. Coping Strategies for Individuals and Families
To cope with the impact of inflation on their cost of living, individuals and families can take several proactive measures. Budgeting and careful financial planning are essential to ensure expenses are prioritized, and savings goals are maintained. Exploring ways to reduce discretionary spending, such as cutting back on non-essential purchases or seeking cost-saving alternatives, can also help alleviate the strain of rising prices. Furthermore, investing in financial literacy and seeking professional advice can empower individuals and families to make informed financial decisions amidst inflationary pressures.
14. Government Measures to Mitigate Inflation’s Impact
Governments play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of inflation on individuals and families. They can implement policies to stabilize prices, such as monetary measures like adjusting interest rates or fiscal policies like managing taxes and government spending. Additionally, governments can invest in social safety nets, such as affordable housing programs, healthcare subsidies, and educational support systems, to alleviate the impact of inflation on vulnerable populations. These measures aim to promote stability and protect the living standards of individuals and families in the face of inflation.
15. Economic Policies to Control Inflation
Effective economic policies are vital in controlling and managing inflation. Central banks often set inflation targets as part of their monetary policy framework. They use various tools to manage the money supply and interest rates to achieve these targets. Additionally, governments can implement fiscal policies, such as adjusting tax rates or government spending, to influence aggregate demand and price levels. Maintaining price stability and controlling inflation is crucial in ensuring the overall well-being and stability of the economy, benefiting individuals and families by preserving their purchasing power.
In conclusion, inflation has a significant impact on the cost of living for individuals and families. It erodes the purchasing power of money and affects various aspects of daily life, including housing costs, food and grocery expenses, transportation costs, healthcare expenses, education costs, savings and investments, wages, and income. It is essential for individuals and families to develop coping strategies to navigate the challenges arising from inflation. Additionally, governments and policymakers have a critical role in implementing measures to mitigate the impact of inflation and promote stability for the well-being of individuals and families. By understanding the relationship between inflation and the cost of living, individuals and families can make informed financial decisions to navigate the ever-changing economic landscape.

