In this article, we will explore the importance of setting financial goals for investing and understanding your time horizon for achieving them. By defining your objectives and identifying the timeframe in which you hope to accomplish them, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial aspirations. So, let’s uncover the significance of setting clear goals and discovering your investment time horizon.
Determining Financial Goals and Time Horizons
When it comes to investing, it is important to have clear financial goals and a defined time horizon. By identifying your financial goals and understanding the time frame in which you aim to achieve them, you can better align your investment strategy and make informed decisions. Whether you have short-term objectives or long-term aspirations, understanding the significance of each goal and the factors that influence them is crucial in setting yourself up for financial success.
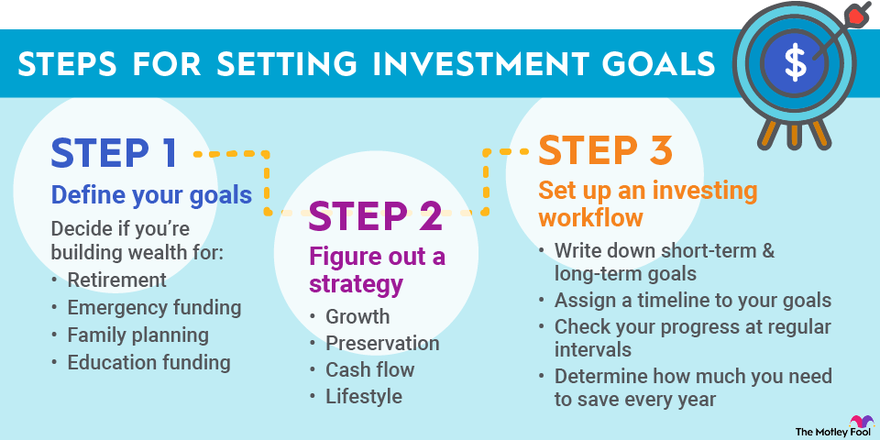
Identifying Financial Goals
To begin, you need to identify your financial goals. These goals can encompass a range of objectives, such as buying a new car, saving for a down payment on a house, paying off debt, or funding your children’s education. It is important to be specific and realistic when setting your financial goals, as this will allow you to create a clear plan of action and stay motivated throughout the process.
When identifying your financial goals, take into consideration both your short-term and long-term aspirations. Short-term goals are typically those you hope to achieve within the next year or two, while long-term goals may be several years or even decades away. By understanding the distinction between short-term and long-term goals, you can better allocate your resources and tailor your investment strategy accordingly.
Defining Time Horizons
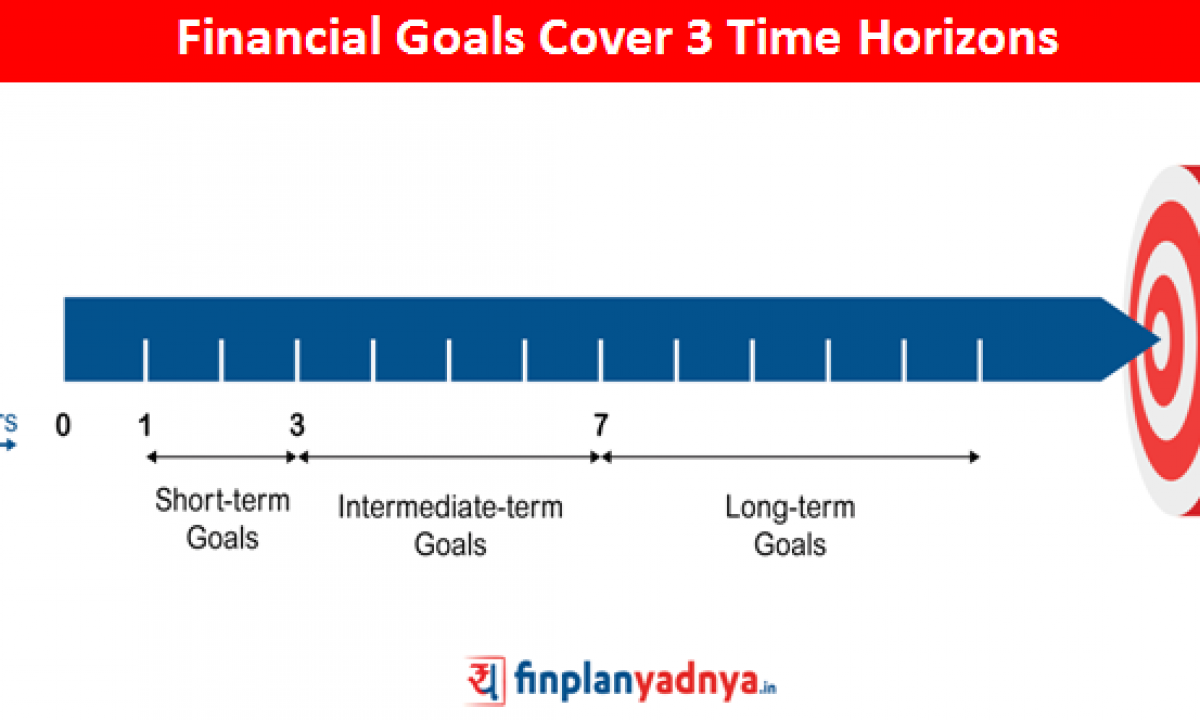
Time horizons play a crucial role in determining the appropriate investment approach for each of your financial goals. Essentially, the time horizon refers to the duration of time you have to reach your goals. It is important to recognize that different goals may have different time horizons and, consequently, will require different investment strategies.
Short-term financial goals have a time horizon of typically less than five years. These goals often require more conservative investment strategies, as there is less time to recover from potential market downturns. On the other hand, long-term financial goals, such as retirement, may have a time horizon of 10, 20, or even 30 years. With a longer time horizon, you are likely to have a higher risk tolerance and can afford to take a more aggressive investment approach.
Short-Term Financial Goals
Importance of Short-Term Goals
Short-term goals are important because they provide the foundation for your overall financial well-being. Achieving these goals can bring a sense of accomplishment and financial stability to your life. Whether it’s saving for a vacation or paying off high-interest debt, short-term goals help you maintain financial discipline and build a solid foundation for future success.
Examples of Short-Term Financial Goals
Examples of short-term financial goals can include saving for a down payment on a house, creating an emergency fund, paying off credit card debt, or taking a dream vacation. These goals are often time-sensitive and require a focused and disciplined approach to achieve them within the desired timeframe.
Medium-Term Financial Goals
Significance of Medium-Term Goals
Medium-term financial goals typically fall within the time horizon of five to ten years. These goals are significant because they bridge the gap between short-term and long-term objectives. Achieving medium-term goals requires careful planning and consistent effort, ultimately setting the stage for long-term financial success.
Examples of Medium-Term Financial Goals
Examples of medium-term financial goals can include saving for a child’s college education, funding a business venture, or upgrading your home. These goals require a combination of short-term discipline and long-term vision, as they often involve larger financial commitments and require a longer time horizon for achievement.
Long-Term Financial Goals
Importance of Long-Term Goals
Long-term financial goals are perhaps the most critical in securing your financial future. These goals typically have a time horizon of ten years or more and often involve accumulating wealth for retirement or ensuring financial security for your loved ones. Long-term goals require a strategic and patient approach to investment, as they allow for a higher tolerance for risk and potentially greater returns over time.
Examples of Long-Term Financial Goals
Examples of long-term financial goals can include saving for retirement, building a substantial investment portfolio, or establishing a charitable foundation. These goals require a long-term mindset and a commitment to consistent contributions to investments or retirement accounts.

Factors Influencing Financial Goals and Time Horizons
Several factors influence your financial goals and time horizons. Understanding these factors is crucial in shaping your investment strategy and ensuring that it aligns with your objectives.
Risk Tolerance
Your risk tolerance refers to your ability and willingness to take on risk in your investments. It is influenced by various factors such as your financial stability, personal circumstances, and comfort level with market fluctuations. A high risk tolerance may allow you to pursue potentially higher returns but also carries a higher level of volatility. In contrast, a low risk tolerance may lead you to opt for more conservative investment choices with lower potential returns but greater stability.
Income Level and Stability
Your income level and stability also play a significant role in determining your financial goals and time horizons. For individuals with higher incomes and stable employment, long-term financial goals, such as retirement, may be the primary focus. Conversely, individuals with lower incomes and less stable employment may need to prioritize short-term goals that provide immediate financial security.
Life Stage
Your life stage, including factors such as age, marital status, and family commitments, can greatly influence your financial goals and time horizons. Younger individuals may have longer time horizons and can afford to take on more risk in their investments, while those nearing retirement may have shorter time horizons and prioritize wealth preservation over growth.
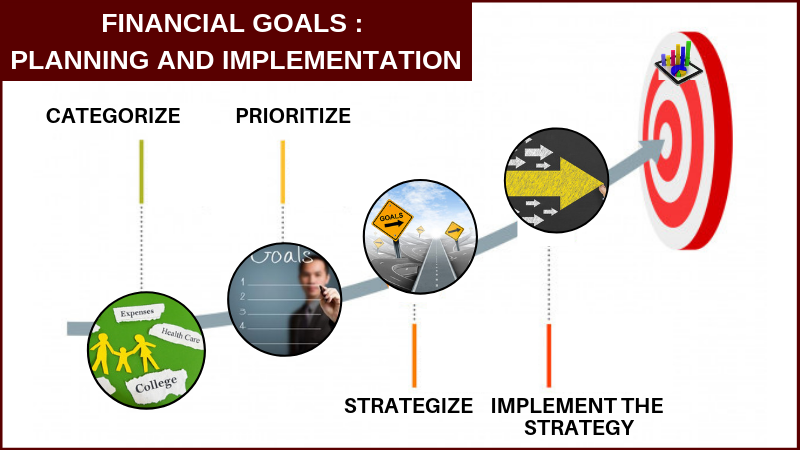
Aligning Investment Strategy with Financial Goals
Once you have identified your financial goals and determined your time horizons, it is essential to align your investment strategy accordingly.
Conservative vs. Aggressive Investing
Conservative investing typically involves a lower risk tolerance and focuses on preserving capital and generating stable income. This approach is well-suited for short-term financial goals or those with a low tolerance for market volatility. Aggressive investing, on the other hand, aims for higher returns through greater exposure to risk. It is often associated with long-term financial goals and individuals with a higher risk tolerance.
Diversification of Investments
Diversification is a fundamental principle in investment strategy that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. By diversifying your portfolio, you can reduce the risk associated with any single investment and potentially enhance returns. Diversification is particularly important for individuals with medium to long-term financial goals, as it provides a balance between risk and potential reward.
Rebalancing Portfolio
Rebalancing your investment portfolio involves periodically adjusting the allocation of your assets to maintain your desired risk and return profile. Over time, certain assets may outperform or underperform, causing your portfolio to deviate from your original asset allocation. By rebalancing, you can bring your portfolio back in line with your goals and ensure that your investments continue to reflect your risk tolerance and time horizons.
The Role of Planning and Budgeting
Planning and budgeting are essential components of achieving your financial goals. By creating a comprehensive financial plan and setting realistic budgets, you can better track your progress and make informed decisions along the way.
Creating a Financial Plan
A financial plan outlines your financial goals, strategies for achieving them, and a timeline for progress. It incorporates your income, expenses, investments, and other key financial factors to provide a roadmap for success. A well-crafted financial plan ensures that you stay focused on your goals and can adapt to changing circumstances.
Setting Realistic Budgets
Budgeting is a vital tool in managing your finances and directing your resources towards your financial goals. By tracking your income and expenses, you can identify areas where you can cut back or save additional funds to allocate towards your goals. Setting realistic budgets allows you to make tangible progress towards your objectives while maintaining financial discipline.
Monitoring and Adjusting Investments
Once you have established your financial plan and implemented your investment strategy, it is crucial to regularly review and adapt your investments to stay on track.
Regularly Reviewing Investments
Regularly reviewing your investments helps you stay informed about market trends, evaluate the performance of your assets, and make necessary adjustments. This can involve analyzing the asset allocation, assessing the performance of individual investments, and considering any changes in your risk tolerance or time horizons.
Adapting to Changing Circumstances
Life is dynamic, and circumstances may change over time. It is important to be flexible and adaptable in your investment strategy to address any shifts in your financial goals or personal circumstances. This may involve adjusting your asset allocation, reevaluating your risk tolerance, or considering new investment opportunities that align with your revised objectives.
Seeking Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice can provide valuable insights and guidance in navigating the complexities of investing and financial planning.
Working with a Financial Advisor
A financial advisor can provide personalized advice based on your unique financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. They can help you assess your financial goals, develop an investment strategy, and guide you in making informed decisions. Working with a financial advisor can give you peace of mind and increase your chances of achieving your financial goals.
Exploring Self-Managed Options
If you feel confident in your financial knowledge and have the time and resources to manage your investments independently, self-managed options may be worth exploring. This can involve researching and selecting investments on your own or utilizing online investment platforms. While self-managing your investments requires a greater level of responsibility, it can provide a sense of control and potentially reduce costs associated with professional advice.
Conclusion
Determining your financial goals and time horizons is a crucial first step in building a successful investment strategy. By understanding the significance of short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals, as well as the factors that influence them, you can align your investment approach accordingly. Incorporating principles such as diversification, regular review, and adaptation to changing circumstances, along with the support of professional advice if needed, can help you achieve your financial goals and secure a prosperous future. Remember, investing is a journey, and by setting clear goals and staying focused, you can navigate the path to financial success.


